The manual for the latest openMSX release can be found on the openMSX home page:
This manual is about openMSX, the open source MSX emulator that tries to achieve near-perfect emulation by using a novel emulation model. You can find more information about openMSX on the openMSX home page. You can also download the emulator itself from there.
openMSX is not complete yet, which means that most things work but not all features have been implemented yet. Many emulation features are implemented, but not all of them are represented yet in the built-in Graphical User Interface. To get the most out of openMSX, we have written this guide.
This manual tells you how you can use openMSX, once it has been installed and properly set up. You should be able to use most of the features of openMSX if you have read it. If you are only using the GUI menus of openMSX, you don't have to pay attention to the exact command and setting names. However it is still useful to read this document to find out how openMSX works and learn its terminology.
Disclaimer: We do not claim this guide is complete or even correct. What you do with the information in it is entirely at your own risk. We just hope it helps you enjoy openMSX more.
For the revision history, please refer to the commit log.
First some terms. Users of real MSX computers will probably not find it hard to understand these, but we'll explain what we mean with them to make sure the terms used in openMSX are clear for everyone.
In this chapter we will tell you how to select MSX machines and how to use extension cartridges, when starting up openMSX.
If you start openMSX without any command-line parameters, you will get the
default machine, which is stored in the default_machine setting. If you did
not change the default machine, the C-BIOS MSX2+ machine will be started.
However, if you created a setup earlier and marked it as the default setup (via the default_setup setting), that setup
will be loaded instead. This can be useful to always start up with your favourite
setup.
To select machines from the GUI, click This will give a window in which you can see an overview of all available machines to select from and hovering on items in the list shows you the most important properties of these machines. You can also filter on type, region or any part of the machine names. You can replace the current machine, or run another machine along the existing running machines. An overview of the running machines is shown at the top of the machine selection window, where you can also change the default machine.
To select a different MSX machine from the command line, you can use the
-machine argument:
It is also possible to use the machine command to switch at run time
in the console, which is explained in
the next chapter.
The C-BIOS machines come with ROMs installed; for other machines you will have to install system ROMs yourself, see the Setup Guide for details. You can always use to verify which system ROMs have been (correctly) installed.
If you have saved a setup earlier (using the GUI via or the store_setup command) you can also use the GUI via to go from that setup. But also
here you can use the command line (via the -setup command line
option) or the console (via the setup command).
Extensions are simply MSX cartridges (extensions to the MSX system) that you can plug into the emulated MSX. openMSX ships with many predefined extensions. Note that many of them require firmware ROMs (called system ROMs); see the Setup Guide for details.
Using the GUI, use the menu where you can either first select the MSX cartridge slot to put the extension into, or directly select the menu option to insert an extension in the first free slot or remove extensions from the slot they're in.
Let's now go into details using the FMPAC as an example. openMSX ships with a
definition (XML file) for the FMPAC extension, but you will have to add the
fmpac.rom firmware ROM yourself. When you have done so, you can
insert an FMPAC into the emulated MSX machine with the following command line:
Similar to machines, you can also use the ext command in the console to do it at run
time. You can also use something like -extb to explicitly specify
cartridge slot B.
If you look in the share/extensions directory (or when using the
console, type the TAB key with the ext command, see next chapter),
you will see all the extensions known to openMSX. For example -ext
mbstereo gives you the MoonBlaster stereo effect: FMPAC on the left
speaker and MSX-AUDIO on the right speaker.
Some of the most used command-line options will be discussed later in this manual. For a complete list of them, type the following command:
Most functionality can now be controlled via the built-in GUI, using the main menu bar as a starting point. This will be sufficient for most users. Originally, this GUI wasn't available and most functionality had to be controlled differently. This way of control is still available (and will remain so); this section will tell you more about it. You don't need to care about any of these commands if the GUI is sufficient for you, but we still recommend having a look at the sections about "Settings" and "Plugging in devices in connectors".
openMSX has a built-in command interface called the console, which allows you to control almost all aspects of openMSX while it is running. To access the console, make sure to have the main emulator window selected, and then press F10 (with default key mapping; Cmd+L on Mac). This will open a window with a command line inside the main openMSX window.
Typing help
gives a list of commands. Using PageUp you can see all of them. If you type
help [command] you will get help for the specified command. This
manual describes a few important commands; a full list can be found in the Console Command Reference. The
console can be used to change disk
images, plug in joysticks or mice, change settings at run time and to change key bindings,
among others. It actually gives you full control of openMSX: if it can't be
done via the console, it's probably impossible!
One very practical feature of the console command line is that you can use "completion" features. Just try typing half a command and then press the TAB key; openMSX will then try to finish the word you were typing or show the possibilities in case of ambiguities. You can use it also for file names, connectors, pluggables and settings, and even for machine and extension names.
The console has very common keyboard controls, similar to most text editors. It also supports copy/paste. Some other controls may be less obvious:
| key(s) | function |
|---|---|
| Up | show previous command from history (starting with current command line) |
| Down | show next command from history (starting with current command line) |
| Tab | attempt completion of current command |
| Enter/Return | execute command line |
You can reset your MSX with the console command reset and exit openMSX with the command
exit. As
explained in the previous chapter, you can change machines with the machine command and
you can insert extensions with the ext command (use tab-completion to see the
list of possible extension names). Remove extensions with the remove_extension command or
get a list of the currently inserted extensions with the list_extensions command. Other
commands will be discussed later on in this manual.
There are many settings in openMSX for customization, changing preferences or enabling extras. The most important ones are in the menu in the GUI. There is also an Advanced item in that menu that will give a huge window with all possible settings. Usually, you can revert a setting to its default value via in the context-menu of that setting.
Using the console, you can use the command set to change any setting. E.g., you can
use it to set the current scaler. Issuing
set with only the setting name (like set scale_algorithm), queries
the current value of that setting.
Settings that have only two possible values can also be toggled with the
toggle
command (an example is the default key binding of F11 to toggle
fullscreen, see also below). A (hopefully) complete list of settings can
also be found in the Console Command
Reference. Note that using the "tab completion" feature can help you a lot
in getting an idea of what settings are possible, as it will only complete
possible options. Just try that.
Let's give a few examples of common settings and how to change them.
If the MSX goes too fast or too slow, adjust the emulation speed with the
speed setting,
which has the speed percentage as parameter. So, typing set
speed 120, will run the emulated MSX at 120% of normal MSX speed.
This is useful for debugging purposes (slow down) or when you want to skip
certain parts of a demo for example (speed up). The GUI has this setting under
.
Some MSX machines like the Panasonic FS-A1GT have built-in software (called
firmware) which can be switched on and off via a switch on the machine itself.
In openMSX the internal software is switched off by default, but you can switch
it on with the following setting: set firmwareswitch on. If the
currently running machine has a firmware switch, a toggle option will show up in
the menu to control it.
If you're not really interested in how long a real MSX would take to load
from diskette, cassette or laserdisc, you could enable the full speed when
loading feature: set fullspeedwhenloading on,
or from the GUI at . It
runs openMSX at maximum speed whenever it thinks that the MSX is loading. The
drawbacks: it might detect a bit too late that the MSX isn't loading anymore,
so sometimes the first notes of music played right after loading might be
fast. Also, when loading openMSX will use all available CPU power to get
maximum speed; the feature has no influence on the state of the MSX, of course.
You can save all your current settings with the save_settings command. At start
up, alternative settings files can be loaded by using the -setting
command-line option. You can also use the load_settings command to load
settings at run time. Settings that are not mentioned in the saved settings
file that you are loading will be untouched. By default, openMSX will
automatically save your settings on exit (whichever way they were changed).
The menu will show you all connectors of the currently running machine and which (pluggable) device is currently plugged in. You can easily plug in other devices there, e.g. a mouse in a joystick port.
Examples of connectors are the joystick ports, the printer port, the MIDI in and out connector, the cassette port, etc. Examples of pluggables are joysticks and mice, but also printers and MIDI equipment.
In the console, you can use the command plug to do this. The command
plug
without any parameters will show a list of connectors and what pluggables are
plugged into them. Using plug [connector] will only show what is
plugged into [connector]. It will come as no surprise that the command plug
[connector] [pluggable] will plug the [pluggable] into the [connector].
Note that using the "tab completion" feature can help you a lot in getting an idea of what plug commands are possible, as it will only complete possible connectors and their possible pluggables. Just give it a try.
The Graphical User Interface (GUI) in openMSX has been built with the Dear ImGui library. It allows the developers to relatively easily build and extend the GUI for all supported platforms. The price we have to pay is that it only works on systems with 3D hardware acceleration support and that it does not look (a lot) like the native GUIs of well-known desktop environments like Windows, macOS, GNOME or KDE.
General help on basic usage of the Dear ImGui features can be found in the menu option.
The current GUI is intended for mouse control. It can (at least partially) also be controlled with a keyboard, but so far this has not been a major focus of development, so this will definitely not be optimal. Control via a game controller is currently disabled, but that may change in future versions.
Although the current openMSX release already has a lot of functionality available via the GUI, it is still incomplete and the user experience could use some love. We appreciate feedback on the GUI a lot and we will try to improve it in later releases based on your input. Please see section 10. Contact Info for more information on how to provide feedback.
Almost all commands and settings available in the GUI have an underlying console command and setting accessible via the console. In several places these underlying commands are mentioned in this manual. Power users especially will appreciate all the ways they can manipulate openMSX with external programs, scripts, or other more advanced methods.
As already mentioned before in this manual, the GUI has a Main menu bar at the top of the openMSX main window. The menu bar fades out when the MSX screen has focus. To get it back, move the mouse cursor to the top of the openMSX window.
![]()
The Main menu bar contains the following top level menus:
If you like, you can even undock the main menu bar from the main openMSX window. This is especially useful if you want to stream the openMSX main window, without showing your interaction with the openMSX menus. Use the triangular icon on the left in the Main menu bar to undock or redock it.
Besides the Main menu bar, some other main GUI elements you are likely to see. Here is a small overview.
The GUI allows you to put any window inside the main openMSX window, or outside of it. But windows can also be docked together, at the (left/right/top/bottom) edge of any window except the main window, even in a tab bar.
The GUI also has specific settings, like shortcuts that can be used in the GUI only.
Also, you can save and load layouts of windows that are combined with each other. This is still a rather rough feature, as it also saves and loads other data, like the history information from some menus.
As an example of a layout, we created one with a debugger focus. The image below shows:
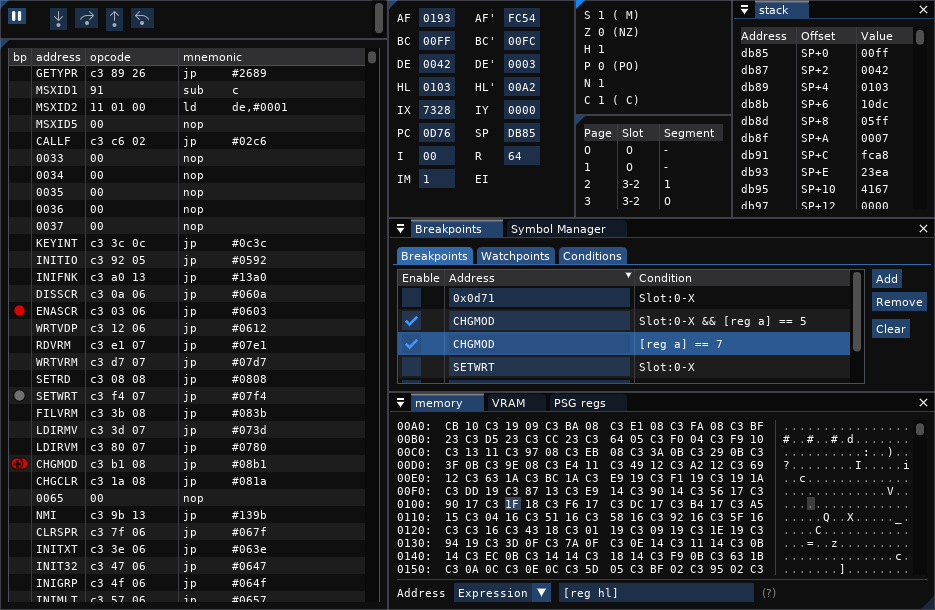
Docking windows can be done in two main ways. Both start by dragging a window over another one. If you do that a popup will appear with 5 sections (middle, east, west, north, south).
In both cases the windows are now grouped, they will move together and minimize together.
The debugger features can require a lot of screen space. Showing everything at once won't be possible (unless maybe if you have a 4K monitor). To accomodate for this, we do try to pay attention to making all openMSX windows compact.
Here are some tips focused on that:
With this information, you can run most of the existing MSX software. If you use the GUI, refer to the menu.
For all supported media files, there is a list of filename extensions that are
recognized by openMSX. If you run openMSX from the command line, adding a file
name (with path if necessary) as a command-line option, openMSX will insert the
file as the proper type of media. The list of supported extensions for each
media type can be easily retrieved with -h option on the command
line. For some media, examples of command-line usage are given below.
If you drag and drop a file with one of these supported extensions into the main openMSX window, openMSX will try to handle it accordingly.
In the GUI you can choose which ROM software you want to run by selecting a Cartridge Slot from the menu. This will open a window where you can tell openMSX exactly what you want to put in the slot, like a ROM image, which mapper to use if the automatically selected one isn't correct, and whether the MSX should be reset after inserting.
And finally, you can also browse for and select (multiple) IPS patches to apply to the selected ROM image. IPS patches are files that describe a modification of the ROM you are applying it to, e.g. a translation or a cheat. This way you do not need to alter the original files.
Using the command line, suppose you want to run the ROM file
galious.rom. Then you simply type:
and the emulated MSX will run the game. (Of course,
in this case, the file galious.rom should be in the current directory.
You can also explicitly indicate that the thing is a ROM image like this:
This lets openMSX know that the file galious.gam is a ROM
cartridge and that openMSX should insert it in the first available free
cartridge slot. You can also use -carta to explicitly specify
cartridge slot A.
In the event openMSX doesn't have the ROM in the ROM database and fails auto
detection of the mapper type, you can specify the mapper to Konami
(for instance) like this:
Note that in practice you won't need this, because most ROM images are in the
database or auto detected if they are not. The -romtype option
should follow the ROM it applies to immediately on the command line.
To apply an IPS patch using the command line, provide the IPS filename like this:
As with the -romtype option, the -ips option on the
command line must follow the ROM file it applies to directly. You can also use
multiple -ips options if you want to apply multiple patches.
If you already have openMSX running and want to insert cartridges at runtime
(maybe even when the MSX is powered on), you can use the carta command in the console as well, which is just as
powerful.
Of course, this can only be done if the running machine has one or more disk drives. From the GUI, simply select the Disk Drive you want to change the disk image for. This will open a Disk Drive window where you can specify what must be in the drive: a disk image (select a disk image file, or create a new disk image), a directory to be used as disk (see next section), a RAM disk (temporary disk image in RAM), or nothing at all. As with ROM images, IPS patches can be selected to be applied.
Disk images in compressed format ((g)zip, xsa) can be used as regular disk images, but do note that they are read-only. Note that in zipped disk images, the first file that is packed into the zip file will be used as disk image.
To specify disk images on the command line, you can type:
for example. Or, if you use a disk image with a filename extension that is unknown to openMSX:
You can also change disks at run-time of course. Just type
in the console to put the specified disk image in drive A. To eject the disk from drive A, use:
Note that inserting another disk image automatically ejects the previous one.
To apply an IPS patch, provide the IPS filename like this:
On the command line, the -ips option must immediately follow the disk image
it applies to. You can also use multiple -ips options if you
want to apply multiple patches.
You can also apply the patches when changing disks at run-time in the console. Just type something like
in the console to put the specified gzipped disk image SDSNAT1C.DSK.gz in drive A, with both IPS patches applied.
The DirAsDsk feature permits you to use a directory on your host computer's file system as a disk image for your emulated MSX. Note that this has nothing to do with harddisk emulation. It simply creates a virtual disk structure in memory from the files that are in the directory that you specified as if it were a disk image. So, on the command line:
will try to put all files of the current directory on a disk image in memory and start openMSX with it. The actual data is still read from/written to the files in your directory so that if you change the contents of the files, these changes are immediately visible in the emulated MSX. This way you can for instance edit source files with your favourite text editor but compile them immediately in the emulated MSX.
Using the default value of the setting DirAsDSKmode (full), all changes to the directory on the host system and on the MSX system are performed, so that they are immediately visible to the other side. If this is not the desired behaviour, please check the documentation of that setting.
Be careful when writing to files from your emulated MSX. In the default 'full' mode, you can change/overwrite/delete/corrupt files on your host system, if you made them accessible for the emulated MSX! Still, this is the behaviour what most people want/expect and it's very useful if you know what you are doing.
Note that MSX disks only have a limited capacity, typically 720kB. If the host directory contains more data, then some host files will be ignored and they will not appear in the virtual disk image.
We do not recommend using real disks (e.g. with a USB floppy drive) with openMSX. There is no specific support for this.
openMSX has a special command to perform file imports and exports, with support for normal disk images, Sunrise IDE harddisk images with partitions (FAT12 only), and Nextor harddisk images with partitions (FAT12 and FAT16).
In the GUI, you can find this tool under . This will open a big window, which has many powerful options. On the left side you select the emulated machine drive (any existing drive, or the "Virtual drive" which only exists in memory). On the right side, you see the host directories with their file content. Use the arrows in the middle to transfer files, the plus button on the left side to create a new (hard) disk image and the directory button to browse for a disk image to insert.
For the console commands that are behind this window, please see the separate manual called Using diskmanipulator.
First thing you need to be aware of: this can only be done on machines that have a cassette port. Most do, but the MSX turboR machines do not, so tape software cannot be used on these machines.
Cassette/tape image file formats that are supported are WAV files (raw digitized recordings of real tapes) and CAS/TSX files. Differences are explained below.
In the GUI select to open the virtual cassette player control window, which allows you to insert a cassette tape image.
To insert a tape image from the console, type:
Once inserted, in MSX Basic, type:
(or another command to load the program on 'tape'.)
The cassetteplayer related commands/settings that are controlled in the tape deck window are:
cassetteplayer rewind, to rewind the tapecassetteplayer eject, to eject the tapecassetteplayer new <filename>, to create a new WAV cassette image to record to; also sets the cassette player in record modecassetteplayer play, to set the cassette player in play mode (when you've just recorded to the cassette)cassetteplayer record, to set the cassette player in record mode, to append to existing cassette images (NOT IMPLEMENTED YET)set cassetteplayer_volume, to set the volume of the cassette player sound (yeah, the screeching tape sounds!)
As you can see in this list, appending to existing cassette images (or
(partially) overwriting them) is not supported (yet). If you want to save
again, just insert a blank tape by using the cassetteplayer new
command again (or the Record button with the circle icon in the Tape Deck
window).
You can also use the so-called CAS files and also TSX files. Use them exactly as you would use WAV files, described in the previous section.
We don't support using CAS files by patching a BIOS natively, because it is not really something we want: we prefer a more authentic emulation without hacks like this. So, the CAS (and also TSX) files are automatically converted to WAV files, internally. Note that the loading time is drastically longer this way (but the setting will help a lot). On the other hand, you will be able to hear the cassette sounds also with these file formats... Admit it, using cassettes with an MSX without those characteristic sounds just wouldn't be the same.
To make it even more comfortable to run software from cassette tapes, check the setting, that will attempt to type the loading instruction for you after the MSX has started up.
Note that saving to existing cassette images is not possible; you can only save to new cassette images in WAV format.
The Sunrise IDE interface was the first one to be emulated in openMSX, so by now it's thoroughly supported. Later support for two types of SCSI interfaces was added: the Gouda/Novaxis SCSI interface and the MEGA-SCSI, followed by support for the MegaFlashROM SCC+ SD, the Carnivore 2, and the Beer IDE interfaces. Not all harddisk management tools may support these newer mass storage devices.
The extensions that enable this have a built-in mass storage (harddisk, SD card, etc.) configuration, in the
form of a 100MB disk image. This is the default size: if the harddisk
image is not present, a file is created with this size. The image will end up
in your openMSX user
directory/persistent/NAME/untitled1/IMAGENAME.dsk, where NAME is
the name of the extension used and IMAGENAME is a name that is configured in
the extension's XML file (e.g. default hd.dsk for the Sunrise IDE).
When using these extensions for the first time, you have to treat them as if
they were real interfaces with a blank harddisk connected. How they should be initialised
depends on the type. We advise you read the manuals, the sections
below give some hints. The diskmanipulator may be helpful, as it
supports harddisk images with both Sunrise IDE and Nextor compatible partition
table formats.
For clarity's sake: since the emulation is done on a big disk image, data corruption of your PC's harddisk is impossible. You will need free disk space for this image, however (default size: 100MB). In other words, you cannot use a normal PC harddisk as an MSX harddisk for these extensions.
The way to use files from your real PC harddisk on an emulated MSX, is by using the DirAsDsk feature. See the DirAsDsk section for more details.
In the GUI under
you can find entries like "Hard Disk A" or "CDROM Drive
A" if such devices are connected to the (IDE/SCSI/SD) extension in your
currently active machine. If wanted, you can also change the used image,
but note that media like harddisks require the machine
to be powered off first (see the menu for the power
setting).
To specify the harddisk image to be used on the command line, use the applicable command-line option, e.g. for Sunrise IDE:
This command gives you the ide extension with symbos.dsk as harddisk
image. You can also change the harddisk image at run time in the console, with a command similar to the diska command:
Please read the following sections for details about the specific extensions.
The extension for this is called 'ide' (shown with the full name Sunrise ATA-IDE in the extension selector). By default it has a harddisk connected to the master port and a CD-ROM player connected to the slave port.
The 'ide' extension needs the BIOS that can be flashed into the Sunrise IDE interface. It can be downloaded from the Sunrise for MSX web site.
The initialisation of a Sunrise IDE harddisk is described in the text files that come with the FDISK program for IDE, downloadable from the Sunrise for MSX web site. There are also some threads on the MSX Resource Center forum that may give you valuable hints.
You can sidestep these procedures by using the diskmanipulator to create an initial hd
image complete with any desired files and subdirectories. For
instance to create a harddisk with 3 partitions of 32 megabyte on it, and have
each partition filled with files and subdirectories, proceed as follows:
Start openMSX with the ide extension, then type in the console:
As announced above, there is (limited) support for CD-ROM with the 'ide'
extension. You can insert an ISO image in that virtual CD-ROM player with the
-cda command-line option and change it at run time with the
cda console
command, all similar to the aforementioned hda and diska commands and options.
The Beer IDE interface, as brought to us by SOLID, is emulated by openMSX, too. This interface only offers a single device (no master and slave) and can only handle up to 4 (version 1.9) or 5 (version 1.8) partitions of 32MB. On the upside, it doesn't need MSX-DOS2, and thus it can run on any MSX (with 64kB RAM to run MSX-DOS). Emulation of this interface should be considered experimental.
Usage is identical to using the Sunrise harddisk interface: you can use the
GUI, the hda command and the
matching command-line parameter -hda to control which image will
be used.
By default, the image is 128MB, so that it can fit 4 partitions of 32MB. Firmware
version 1.9RC1 is selected by default, because we could not get the 1.8
firmware to work: the MSXFDISK program didn't create partitions which actually
worked with the 1.8 firmware. If you want to experiment with it, you can change
the firmware to use by editing the extension file in
share/extensions/Beer_IDE.xml.
With the 1.9RC1 firmware, you can use diskmanipulator to create a harddisk
image and import from and export to them. To get started, partition the default
drive with diskmanipulator partition hda -dos1 32M 32M 32M 32M.
Then import MSX-DOS system files onto the first partition using
diskmanipulator import hda1 <host-path>, and now you should
be able to boot into MSX-DOS.
Unfortunately, the Beer IDE is hardly documented and the software is hard to find. So, it's for experts only!
First of all: the SCSI emulation is experimental! There is a lot bigger chance that you may lose data on your emulated harddisk images with SCSI than with Sunrise IDE! When we tried it, everything seemed fine, but you have been warned.
The SCSI extensions (currently Gouda_SCSI, ESE_MEGA-SCSI and ESE_WAVE-SCSI) have the default 100 MB harddisk image connected on target ID 1 and an (even more experimental) LS-120 device (basically a harddisk like media that can be changed/ejected when the power is on) on target ID 2.
Specifying or changing harddisk images works the same as with IDE, see above.
To change the disk image of the LS-120 device, use the lsa (LS
drive A) command, exactly the same as the hda command. Of course you do not need to have the
power turned off to do this, as this is the whole point of the LS-120 device.
You can also just eject it, with the eject subcommand. At the time
of writing there seems to be a bug when doing this: the device isn't listed in
the device list if there is no media inserted. It is currently not possible to specify an
LS-120 device on the command line.
Initialisation for the ESE SCSI devices needs tools like MGINST,
which can be found on Takamichi's web site.
They include small manuals in English. This manual is not the place to explain
the procedure, but the idea is as follows. First, install the MSX-DOS 2 kernel
in the SRAM of the device, using the MGINST program (you might
want to use KSAVER first to save the kernel of your DOS 2
cartridge). After this, the MSX will boot from the SRAM disk. Use the
SFORM-1 (for MSX-DOS) or the SFORM-2 (for MSX-DOS 2)
to format the drive (use a physical format, for now). Use ESET to
assign drive letters to partitions.
For the Gouda (Novaxis) SCSI interface, you need the Novaxis ROM, see also Hans
Otten's Page or The Ultimate MSX FAQ. Those sites
also contain manuals for the Novaxis ROM. Initialisation is done with the
NFDISK utility, which can be found on Marcel Delorme's site (archived).
Currently there is only one SD interface emulated: the MegaFlashROM SCC+ SD. All features of this cartridge are emulated in the sense that all software currently working with it, runs on openMSX too. It is not emulated accurately enough to rely on it for development.
The SD card slots appear in the openMSX user interface as "Hard Disk A/B" and hot plugging is not supported. So, it shows up almost identically to the Sunrise IDE interface.
The difference compared to a real MegaFlashROM SCC+ SD, is that the extension does not
come with anything flashed on the flash ROM by default. There are two ways to
overcome that. The first one is to download the preflashed ROM content (for URL
see below) and install it into your systemroms folder, like any usual system
ROM. This only works if you use the extension for the first time, unless you
manually delete the persistent file for the flash ROM chip (typically in your
openMSX user
directory/persistent/MegaFlashROM_SCC+_SD/untitled1/megaflashromsccplussd.sram).
Only if no such file is found, openMSX will load the content of that ROM file
into the flash ROM of the MegaFlashROM SCC+ SD. The second way is manually
flashing things like Nextor, the rescue menu and the ROM disk. This is all
described in the manual (see at the end of this section) of the MegaFlashROM
SCC+ SD, because on a real device you may also need to do this.
Once you achieved this, usage is again identical to using the Sunrise harddisk
interface, so in the console you can use the hda/hdb commands and the matching command-line
parameters -hda and -hdb to control which image will
be used for the first and second SD card.
Currently, by default, the first SD card is 8MB and the 2nd SD card is 100MB in
size. You can change these defaults by editing the extension file in
share/extensions/MegaFlashROM_SCC+_SD.xml. For formatting and
managing the SD cards, please refer to its manual and tools on the Flash part
of the MSX
Cartridge Shop. It also provides the ROM file with the initial content of
the flash ROM as it is shipped on real MegaFlashROM SCC+ SD cartridges.
To get files on the SD cards, you can use diskmanipulator with the
-nextor option to partition and to import files, similar to what
is explained above in the Sunrise IDE
section.
In order to run Laserdisc software, you need to have this optional feature compiled into your openMSX binary. Laserdisc is only supported by the Pioneer PX-7 or the Pioneer PX-V60 machines, which have special hardware to control the laserdisc player.
The Laserdisc image can be selected under or in the console, type laserdiscplayer insert <file>.ogv
to insert a Laserdisc (image) into the Laserdisc player. By default, the Laserdisc will be loaded automatically. If the autorunlaserdisc setting is off, then you will have to take a few steps yourself.
After booting the MSX, choose option 1 when asked if you want to run P-BASIC (Palcom-BASIC). In MSX-BASIC, type:
to load and run the Laserdisc program.
The program is encoded on the right audio channel, which will not be audible.
With set fullspeedwhenloading on,
openMSX runs at maximum speed whenever the Laserdisc is seeking or loading a
program.
The special MSX keys are mapped as follows, the first column for PCs (running Windows, Linux or BSD), the second column for Apple Macintosh computers:
| MSX key | key (PC) | key (Mac) |
|---|---|---|
| CTRL key | L-CTRL | L-CTRL |
| dead (accents) key | R-CTRL | R-CTRL |
| GRAPH key | L-ALT | L-ALT |
| CODE/KANA key | R-ALT | R-ALT |
| 取消 ('cancel') key | L-Windows | |
| 実行 ('execute') key | R-Windows | |
| SELECT key | F7 | F7 |
| STOP key | F8 | F8 |
| INS key | Insert | Cmd+I |
The ColecoVision controllers are mapped as follows:
| direction/key | player 1 | player 2 |
|---|---|---|
| up | cursor up | W |
| down | cursor down | S |
| left | cursor left | A |
| right | cursor right | D |
| fire left | space, R-CTRL | L-CTRL |
| fire right | L-ALT, R-ALT, R-SHIFT | L-SHIFT |
| 1 | 1, numpad 1 | R |
| 2 | 2, numpad 2 | T |
| 3 | 3, numpad 3 | Y |
| 4 | 4, numpad 4 | F |
| 5 | 5, numpad 5 | G |
| 6 | 6, numpad 6 | H |
| 7 | 7, numpad 7 | V |
| 8 | 8, numpad 8 | B |
| 9 | 9, numpad 9 | N |
| 0 | 0, numpad 0 | U |
| * | -, numpad *, numpad - | J |
| # | =, numpad /, numpad + | M |
Host joysticks can also be used for directions and the fire buttons, but the keys from the telephone-style keypad can only be entered via the host keyboard.
The mapping of the keys for emulator functions is fully customisable using the
bind command in
the console. Your customised key
bindings are saved together with the settings. This subsection lists the
default key mapping.
| keys (PC) | keys (Mac) | function |
|---|---|---|
| Pause | Cmd+P (Pause) | Pause emulation |
| ALT+F4 | Cmd+Q (Quit) | Quit openMSX |
| CTRL+Pause (Break) | Quit openMSX (not in Windows) | |
| PrtScr | Cmd+D (Dump) | Save current screen to a file (screen shot) |
| PageUp | PageUp | Go 1 second back in time, using the reverse feature |
| PageDown | PageDown | Go 1 second forward in time, using the reverse feature |
| F9 | Cmd+T (Fastforward) | Toggle fastforward mode (normal vs fastforward speed) |
| F10 | Cmd+L (consoLe) | Toggle console display |
| F11 or ALT+Enter | Cmd+F (Full) | Toggle full screen mode |
| F12 | Cmd+U (mUte) | Toggle audio mute |
| ALT+F7 | Cmd+R (Restore) | Quick loadstate (from 'quicksave' slot) |
| ALT+F8 | Cmd+S (Save) | Quick savestate (to 'quicksave' slot) |
| CTRL+Win+C | Cmd+C (Copy) | Copy screen's text content to clipboard |
| CTRL+Win+V | Cmd+V (paste) | Type the text from the clipboard into the MSX |
Note that Mac users must use GUI as a modifier for the Command
(Apple logo) key. On PC's use GUI for the Windows key.
Please note that openMSX is currently intended to be mouse controlled. Some parts of the GUI can also be controlled via keyboard, but this has not been optimized at all for now. Control via gamepad is currently disabled (this might change in a future version).
This section is about how host computer keyboard layouts are mapped to MSX keyboard layouts. This is mostly interesting if those differ (a lot). For example, you have a US-English keyboard on your PC and you are emulating a Japanese MSX computer. Or, you have a Japanese Mac and you are emulating a Spanish MSX computer.
There are features to make this as smooth as possible, so that you can use your own keyboard for any kind of MSX with as little surprises as possible. The trick is the new character-based mapping mode, which tries to convert any character you enter with your host computer's keyboard to an MSX key press. For this feature, all MSX hardware configuration files now have information about their keyboard layout. Anyway, this mapping mode is enabled by default, so you don't have to do anything to make this work!
However, there are always some pesky details. For those details we refer to the documentation of other keyboard settings, where they are explained in full detail: mapping mode (as mentioned before), kbd_numkeypad_always_enabled (use numerical keypad even when your MSX doesn't have one), kbd_code_kana_host_key (specify an alternative host key for CODE/KANA) and kbd_numkeypad_enter_key (specifies mapping of the ENTER key of the keypad).
You can find the mapping mode setting in .
If you have a controller or joystick connected to your PC, you can map its
input to one of the emulated MSX joystick (like) devices, internally called msxjoystick1,
msxjoystick2, joymega1 and joymega2.
See the earlier section about plugging devices on how to connect these devices to your emulated machine.
The mapping of your host devices (host controllers, joysticks or keyboard) to these 4 emulated MSX joysticks is fully configurable. The easiest way is to use the GUI menu for that under . You can also do it in the console with the msxjoystick<n>_config/joymega<n>_config settings.
Most modern joysticks have more buttons than the 2 buttons that are defined by
the MSX standard. Therefore a lot of games use extra keys on the keyboard for
extra functionality. For instance, almost all Konami games use F1 to pause
the game. You can assign this extra functionality to your joystick by using the
bind command. As
an example here is how to map button 4 of the first joystick to the F1-key,
button 5 to F2, ...
For a more detailed explanation of this command see the Console Command Reference. Please note that unfortunately, such mappings are not configurable via the GUI menu.
To connect a mouse, you can also use the menu or the plug command: plug joyporta mouse
will connect a mouse to joystick port A. If you want the joystick emulation
feature that some mice (like the Philips SBC-3810 and the Sony MOS-1) have,
keep the left mouse key pressed when plugging it in, just as on a real MSX.
If you are using openMSX in windowed mode, it might be tricky to use the mouse.
The setting: set grabinput on
makes sure all input goes to openMSX. Your cursor cannot leave the openMSX
window with this setting. Just turn it back to off, if you want to disable this
again. If you only want to escape the window briefly, use this command:
escape_grab. It permits you to
leave the window, but the next time you enter it, the cursor is grabbed again.
It might be a good idea to bind this command to a key, using the bind command, which is
mentioned above. You can also toggle the setting via .
The Arkanoid games by Taito both have support for a special Arkanoid game pad,
with a classical rotary knob to control the position of the bat. This device
is emulated as well and can be controlled by the mouse. Plug it via the GUI
menu or in
the console with plug joyporta arkanoidpad
.
Some MSX trackballs like the HAL CAT and the Sony HB-G7B seem to have identical hardware
and are also emulated by openMSX, again using the mouse to control it. In MSX
software, the trackball is mostly supported in port B only. Using the console
you can use therefore plug joyportb trackball.
Quite some HAL programs have support for it, e.g. Hole in One, Eddy II, Music Studio G7, Space Trouble and Super Billiards. The test program provided in the Sony HB-G7B service manual also works fine, of course.
Some MSX touch pads like the Philips NMS 1150 Graphic Tablet are also emulated
by openMSX, again using the mouse to control it (where mouse button 1
corresponds to touch or no touch and mouse button 2 to the button on the pen of
the touch pad). Also the touch pad is mostly supported in port B only, so the
console command is plug joyportb touchpad
This device is mostly supported by the Philips drawing programs Designer, Designer Plus and Video Graphics (all in port B) and by Pioneer MSX Video Art (port A).
Note that the whole openMSX window will function as the surface of the touch pad. This may not align with the actual pixels of the screen in that window, see the touchpad_transform_matrix setting for how to adjust this.
Sony made a small dongle for game testers to cheat within the games. The games
that have support for it will check if the UP and DOWN keys are pressed. The
magic key is supported by these games in port B only (console: plug joyportb
magic-key.
Known games that can use this Magic Key are:
The Ninja Tap (忍者タップ) is an adapter designed by Knight's chamber and
sold in Japan by PCCM. This adapter allows you to use up to 4 joysticks per port.
Plug it via the GUI or with the console using plug joyporta ninjatap.
Tetris 2 Special Edition from R.A.M., an Italian MSX group, needs the dongle in
port B too start the game. So, on the console use plug joyportb tetris2-protection
The MSX paddle controller is a quite simple device, but there are not so many
commercial implementations for MSX. The Yamaha MMP-01 is a music pad that is
known to use this protocol to transmit its coordinates. Plug it in the console
as follows: plug
joyporta paddle.
Circuit Designer dongle from The Falcon, needs the dongle in port B to start
the program, so in the console type: plug joyportb circuit-designer-rd-dongle
.
openMSX uses the OpenGL graphics library for all post processing (hence the PP in SDLGL-PP, which is the name of the "renderer", the software component that generates the graphical part of the emulation, the MSX 'screen'). This includes scalers and other effects, but also the GUI... Because of all this, openMSX runs best with a hardware accelerated OpenGL library. See the Setup Guide for OpenGL performance tips. So, again, be aware that openMSX requires both your video card and video driver to support at least OpenGL 2.0. Sometimes you need to upgrade your driver to make it work. If your videocard or driver don't support OpenGL 2.0, openMSX will not start up and report an error.
Most video related settings can be found under the menu.
The rest of this section describes more details about the settings you can find
there. For instance, for full screen mode, there is a checkbox in that menu,
which maps to the fullscreen setting.
Most MSX screen modes are only 256×212 pixels big. This is quite small
for today's PC screen resolutions. That's why you have the possibility to
scale up the image. There are currently three possible scaling factors: 2, 3
and 4. If you select 2, all MSX pixels are mapped to a 640×480 pixels PC
window, for 3 to a 960×720 pixel window and for 4 to the obvious
1280×960 window. The setting which determines this is called scale_factor. In
general, the higher the factor, the better the output image is.
There are also a number of scaling algorithms (setting scale_algorithm) that can be
set. The scaling algorithm determines how exactly the mapping is done between
the MSX input screen and the PC output screen. As we render more pixels than
the normally visible MSX pixels, this allows for extra possibilities in the algorithms, like
deinterlacing and adding scanlines, blur, anti-aliasing (rounding of blocky
patters like stair cases) or even a Trinitron-like TV effect.
openMSX contains the following scaling algorithms:
blur setting. This algorithm also includes
scan lines.
A small (somewhat outdated) demonstration of some of the algorithms can be found on the openMSX web site.
PC monitors can have different gamma values than MSX monitors.
To compensate for this, openMSX has a gamma correction feature.
It is controlled by the gamma setting.
A value of 1.0 disables gamma correction; a lower value makes the image darker;
a higher value makes it brighter.
If you want to know what gamma correction really means, read this page about monitor gamma. The gamma correction value you can set in openMSX should be the gamma of your PC screen divided by the gamma of the MSX screen. I measured the gamma of my PC screen (TFT) at 2.0 and the gamma of my MSX monitor at 2.5. That puts the gamma correction at 2.0 / 2.5 = 0.8. So if I enter that value, the openMSX image will have comparable brightness to the MSX image. However, 0.8 is not the value I'm actually using: I prefer a brighter image than my MSX monitor, so I chose to use a gamma correction of 1.1.
openMSX contains a couple of special effects settings that can be applied to the video output:
deinterlacedeinterlace setting controls this
feature:
it can be on (enabled) or off (disabled); it is enabled by default.
deflickerscanlinesimple, tv or RGBTriplet is used.
blurblur
settings control this:
0 means no blur (completely sharp), 50 means some blur (like a monitor),
100 means maximum blur (like a TV).
All other values between 0 and 100 are also possible of course.
This feature is disabled when a scaling algorithm other than
simple or RGBTriplet is used.
glow)glow setting
controls the amount of after glow:
0 means no after glow, 100 means maximum after glow.
noisenoise
setting controls the amount:
0 means no noise, 100 means maximum noise. The value is actually the deviation
of the colour of the original pixel and non-integer values are also possible.
display_deform)normal: no deformation (default)3d: emulates a 3D view on an arcade cabinet's screen
An advanced setting (which you can find under
(the accuracy setting) controls how often
the renderer is synchronised with the MSX video processor (VDP).
There are three options:
openMSX has GFX9000 emulation. As there isn't that much software for it available, it is not as complete, functional and optimized as the video emulation of the classical MSX chips. Despite of all this, most existing GFX9000 software runs pretty well, so we found it worth sharing with you anyway.
The real GFX9000 has an external video connector to which you can connect a
second monitor. We never took the trouble to
emulate a second monitor, however, so to see the GFX9000 in action, you need to switch the
videosource setting, which mimics a so-called SCART-switch in the real
world: set
videosource GFX9000.
This setting is only available when there are actually multiple video sources
available. In the GUI you can find it under .
Alternatively, instead of the GFX9000 extension, you could use the Video9000 extension (also built in in several Boosted MSX machine configurations). The Video 9000 hardware has the possibility to superimpose the GFX9000 video on top of the V99xx video (and this is practically the only feature of the Video 9000 that is currently implemented). Software that is Video 9000 aware, will tell the Video 9000 to show the GFX9000 if something interesting is to be seen on the GFX9000 video output. So, for such software, you do not have to switch video sources if you simply use the Video9000 video source. When a Video 9000 is present in the currently running MSX configuration, the Video9000 video source will be selected by default, to make use of this superimpose feature. For programs not aware of Video 9000, you will still have to switch video sources manually, just like on a real system.
To get your normal MSX screen back, set the setting back to MSX. If you want to
toggle between them with a hotkey, it might be useful to bind a key for it. E.g.: bind F6 cycle videosource.
cycle is a Tcl
command that cycles through the options of the setting in the parameter.
The video recorder enables you to record the audio and video rendered by
openMSX to an AVI file. The output video is in 320×240 resolution by
default, at 640×480 when using the -doublesize flag and at
960×720 when using the -triplesize flag. The video is
compressed with the ZMBV codec, a fast lossless compression algorithm that
works very well on 2D computer generated images. The FAQ contains more information about this codec. The
audio is uncompressed.
The recorded AVI file will not suffer from any hiccups, even if the emulation
ran too slow when you recorded it. The current video source (see previous
section) is recorded and the sound is recorded with the current frequency setting.
If you change the frequency setting during recording,
or, more importantly, if the software changes from PAL (50 Hz) to NTSC (60 Hz)
during recording, the video will get out of sync with the audio. Most of the special effects will not be recorded.
If any stereo sound devices are present or any sound device has an off-center
balance, the recording will be made in stereo, otherwise it will be mono. If
a recording is made in mono and then a stereo sound device is added, you'll
receive a warning that stereo sound has been detected and that the two
channels will be mixed down to mono. You can prevent this from happening by
using the -stereo option to force a stereo recording even if
no stereo devices are present at the time you enter the command. You can also
force a mono recording with -mono to save space.
In the GUI you can find the video recorder under , which will open a the corresponding window, in which you can specify all the above mentioned settings.
In the console, you can use the command record start to record to a default file
name, or you can use an additional parameter to specify a file. The command
record stop
stops recording and record toggle toggles it. You can use
the -audioonly or -videoonly option to record only
sound or video.
If you want to put a recorded video on your web site, it is better to transcode
the audio to MP3 or Vorbis format, as this makes the file a lot smaller.
YouTube supports the ZMBV codec, so if you want to upload your recording you do
not need to transcode the video. If you want to share your video with people
who do not have (or want to install) the ZMBV codec, you should still transcode
it, of course. This can be done with programs such as Virtual Dub (Windows) or MPlayer's MEncoder
(Linux/UNIX). For YouTube you may want to use the command record_chunks instead:
it will enable you to chop up your video in several parts and enables
-doublesize automatically.
Recording as explained above will happen in real-time. This can be annoying if
you want to make a demonstration video, because you all mistakes will be
recorded as well. To work around this, you can also use the reverse feature during
the scene you want to record. After the scene, reverse to the beginning, start
the recording as explained above and let the scene replay relaxedly. You can
even speed it up using the throttle setting. This method of recording is
also useful when real-time recording has a big impact on the performance of
openMSX on your hardware. See also the
chapter about this feature.
Most audio related settings can be found under the menu.
There is a master_volume setting, which
controls the overall output volume of openMSX (it applies to all sound
devices). Volume 0 means no sound, volume 100 is maximum.
There is also a mute setting, to disable all sound from
openMSX at once. It can be on (muted) or off (sound is audible). By default,
mute is bound to the F12 key.
There are also settings for each emulated sound device. These can be found under the option in the menu.
For each sound device there is a volume setting.
Volume 0 means no sound, volume 100 is maximum. In the console you can do this, for example: set "MSX Music_volume"
50.
For each sound device, you can control the distribution of the sound output of
this chip over the left and right channel, with the balance setting. This is
very similar to the balance knob on (older?) hifi equipment.
Example: set PSG_balance -100, which sets
the PSG entirely to the left channel. Any sound device can also be individually
(un)muted using the mute_channels command.
If you'd like to apply some special effects to the PSG sound, you should take a look at the vibrato and detune (both percent and frequency) settings.
Currently, openMSX supports the following MSX MIDI interfaces:
To use MIDI, start openMSX with a machine that has a MIDI interface built in, or add one of the mentioned MIDI interface extensions. Then plug a MIDI out and/or MIDI in device into that MSX MIDI interface using the GUI menu or the openMSX console.
You can connect the MIDI out of the MSX to a host MIDI device, such as a
physical MIDI out port, a soft synthesizer or a sequencer program. On Windows,
Linux and macOS, host MIDI devices are made available as pluggables in openMSX.
On macOS, you can opt to instead select Virtual OUT to create a
virtual MIDI port for Mac MIDI software to connect to.
For example, use the machine Panasonic_FS-A1GT and plug into the
Munt soft
synthesizer (MT-32 emulator) using menu, or with the console command plug msx-midi-out Munt\
MT-32.
The exact naming of the host MIDI devices differs per platform. In the console
you can use tab completion to see the options: type plug
msx-midi-out and hit TAB twice.
The midi-out-logger MIDI device is available on all platforms and
logs MIDI events to a file.
You can specify the file to log to using set
midi-out-logfilename.
The log is a raw binary log of the bytes written by the MIDI interface, with no
timing information. Therefore its usefulness is mostly limited to debugging.
On UNIX-like systems, it is possible to log to a MIDI device node, for example
/dev/midi and configure the sound system to send those notes to a
soft synthesizer. This is harder to configure than using for example the ALSA
MIDI out device, so it's only recommended when no platform-specific MIDI
devices are available in openMSX. On MSX Resource Center there is a
forum thread which describes how to connect openMSX to Timidity via
/dev/midi.
Vice versa, the MIDI in port can also receive data from the system by plugging
a device into msx-midi-in (for the Panasonic FS-A1GT; use the
appropriate connector name for other devices). Analogous to the above mentioned
outputs you can connect a midi-in-reader which reads from a file
or /dev/midi on Linux. On Windows and macOS available MIDI devices
show up as separate pluggables. On macOS a Virtual IN port is
available as well.
openMSX records the sound at the exact speed at which it should be produced, no matter the speed at which the emulation was running while recording. Note that recording sound to the uncompressed WAV format will take a lot of disk space: at 44.1 kHz it will take about 176 kB per second.
In the GUI you can find the audio recorder under , which will open a the audio/video recording window. Just select to log to said WAV file.
The underlying console command to start the recording of sound is soundlog start. It
will automatically choose a file name and save it in the soundlogs
directory in your personal openMSX folder. You can also add an extra parameter
to specify the filename for the new WAV file. To stop recording, use soundlog stop. You
can toggle the recording status using soundlog toggle, which is useful if
you bind this
command to a hotkey.
There is also an advanced feature for recording audio to file: you can record
individual channels of sound chips to individual files on disk. The sound is in
the native frequency of the sound chip this time, which means that for chips
like PSG or SCC (which run at very high frequencies), the files will be huge.
(You have been warned!) This feature can be controlled in the GUI via and in that window click on the "channels" checkbox,
which opens a window where you can fill in a file name for each channel you
want to record with. Perhaps it is easiest to control from the console with the
record_channels command. Note
that in contrast to the soundlog command, the output file of
this command ends up in the current directory and not in a special directory.
We hope you can use this command to study the fantastic compositions of MSX
software and make great remakes of them.
A feature of emulators which is particularly useful is saving the state of the emulated machine to a file, in order to load it again later and continue exactly where you left off when saving. Not only useful for games, but also for debugging or testing. For openMSX we designed this feature in such a way that it is trying really hard to be future proof. So, you don't have to be afraid to upgrade to a new version of openMSX: your save states will remain usable!
In the GUI's menu you find all options to (quick) load and save states and even more.
The easiest way to use it is by using the keyboard shortcuts for quickly saving
and loading a state, see the shortcut hints in the aforementioned menu and also the key mapping
section. These shortcuts basically use the savestate and loadstate commands, with the
parameter quicksave, i.e. they use a savestate file with the name
'quicksave'. You can also use the commands directly yourself, with the argument
as the name of the slot you save the state to (use TAB or the list_savestates
command to see your previously saved states). Without having to browse the file
system of your computer, you can also conveniently delete existing save games
with the delete_savestate command.
Note that when saving the state of the machine, a screenshot will also be saved with it, so that those could be used for save state browsing.
Inspired by the meisei MSX emulator, openMSX also has a reverse feature. This enables you to go back in MSX time, so you can correct mistakes in your game play or you can watch what you did (and also record a video of it).
You can go back in time a second using the key binding for this: PageUp. Once you went back, openMSX will replay whatever you did when you were at this time for the first time, until it got at the point where you went back. From then on, everything will continue as normal. If you touched any control of your MSX during replay, you have indicated to take over from the replay. If you do that, the rest of the replay is erased (openMSX forgets that that future ever happened). This is the typical way to correct mistakes using this feature.
While replaying, you can also jump forward in time ("Back to the Future") using
PageDown. Also, you can go back a specific amount of seconds or to an absolute
moment in (MSX) time, all using the reverse command. (This can also be
useful when you're developing/debugging MSX software.)
If all of this sounds a bit confusing, you can use the reverse bar (by default, it's placed in the bottom right corner, hover there in the main openMSX window to make it appear), which will show you a visualisation of all of this on screen. The bar represents the time while the feature was enabled and shows the current moment in time (the red indicator). You can click on it to jump back and forward in time. The vertical lines indicate times when snapshots were made. The bar will fade out after a while, but hovering your cursor over it makes it reappear. If you want to get rid of the bar, toggle this setting in the GUI menu: . (This will not turn off the reverse feature itself.)
If you want to disable the reverse feature, you can use or the underlying reverse stop console command.
And if you don't want it to restart again anymore, uncheck the setting.
If you want to save a very compact recording of what you did, or want to have
the possibility to start off in the middle of a recording, you can save your
complete replay to a file with or the reverse savereplay command. They can
also be loaded of course, with or reverse loadreplay.
openMSX includes a game trainer system. You start with it by using the GUI menu: This will open a window in which you must first select the game you want to use a trainer for from the list of supported games. When a game is selected, you see the list of cheats displayed for the game, where you can also toggle the different cheats you want to activate.
As with most openMSX functionality, the trainers can also be used from the console, and even there it is very easy to
use. As always, you could type: help trainer, for some basic help.
Suppose you want to cheat on Metal Gear. Then it would be useful to type:
trainer Metal[TAB], which will expand to: trainer Metal\
Gear. When you then press enter, you see which cheats are available in
the Metal Gear trainer. You can activate them by typing e.g.: trainer
Metal\ Gear 1 2 3 4. This will activate (toggle) the first 4 cheats (as
the list will tell you which is printed after the command: the crosses indicate an
active cheat). You can also use the descriptions instead of the numbers:
trainer Metal\ Gear "enemy 1 gone" "enemy 2 gone". Or, if you want
to activate all cheats you can simply type: trainer Metal\ Gear
all.
If this sounds a bit difficult for you, just try it out. It's really much easier when you actually work with it. As always in the console, using TAB to complete your commands and their options proves to be very useful!
This chapter describes how an MSX programmer can use the openMSX built-in debug device. This is an artificial MSX device that is connected to an MSX I/O port. It can be used to send debug messages to the host operating system.
Note that openMSX also contains built-in debugging functions, which can be
accessed with the debug console command. With that debugger
you can read and write all registers and memory of almost all devices that are
supported in openMSX. It also supports break points, watch points and stepping.
See the menu for the most common debugging options.
To enable the debug device, insert the debugdevice extension. To
do this when starting openMSX, simply add -ext debugdevice to the
openMSX command line. If openMSX is already running, you can use the
ext
console command.
You can use the Debug Device output setting to specify the
file name to write the debug output to.
Controlling the device is done from within an MSX program. For this purpose, the output ports 0x2E and 0x2F are used. The first port is the Mode Set Register. Bytes sent to this port have the following meaning.
| bit(s) | meaning |
|---|---|
| 7 | unused |
| 6 | line feed mode (0 = line feed at mode change, 1 no line feed) |
| 5-4 | output mode (0 = OFF, 1 = single byte, 2 = multi byte) |
| 3-0 | mode-specific parameters (see below) |
When using mode 1, single byte mode, the lower 4 bits each enable a particular output format:
| bit(s) | meaning |
|---|---|
| 3 | ASCII mode on/off |
| 2 | decimal mode on/off |
| 1 | binary mode on/off |
| 0 | hexadecimal mode on/off |
So, every parameter bit turns an output format on or off and more than one output format can be specified at the same time.
The parameters for mode 2 (multi byte mode) are as follows:
| bit(s) | meaning |
|---|---|
| 3-2 | unused |
| 1-0 | mode (0 = hex, 1 = binary, 2 = decimal, 3 = ASCII mode) |
In mode 1, any write to port 0x2F will result in output. This way, the
programmer can see if a specific address is reached by adding a single
OUT to the code. The output depends on the parameters set with the
mode register. Each bit represents a specific format, and by turning the bits
on and off, the programmer can decide which formats should be used.
Here is an example:
LD A,65 OUT ($2f),A
This will give the following output:
41h 01000001b 065 'A' emutime: 36407199578
(when all bits are on, mode register = 0x1F)
or
41h 065 'A' emutime: 36407199578
(when the binary bit is off, mode register = 0x1D)
or
41h emutime: 36407199578
(when only the hexbit is on, mode register = 0x11)
and so on.
The EmuTime part is a special number that keeps track of the openMSX emulation. The larger this number is, the later the event took place. This is a great way to get an idea of the timing of things.
If the character to print is a special character, like carriage return, linefeed, beep or tab, the character between the ' ' will be a dot (.) and the normal character is 'displayed' at the very end of the line, so it won't mess up the layout of the whole line.
Unlike mode 1, the data in this mode is always shown in one mode only. It's either in hex mode, binary mode, decimal mode or ASCII mode, but never a combination. Also the EmuTime bit is left out.
Here is an example:
LD A,xx OUT ($2e),A LD A,$41 OUT ($2f),A OUT ($2f),A OUT ($2f),A
If we substitute $20 for xx, we get:
41h 41h 41h
and if we substitute $22 for xx, we get:
065 065 065
The extra zero is added to keep alignment. Finally, if we want ASCII
output, all we need to do is change xx for $23:
AAA
In this special case, the space in between the data is left out. Any special character like carriage return, linefeed, beep or tab will be printed as you would expect.
This chapter describes briefly the built-in programmable device, a resource that could prove useful for driver or hardware developers writing and debugging software on openMSX instead of a real MSX. The programmable device is a virtual MSX device that can be connected on the fly to a user-defined list of I/O ports. It can be used to create a two-way communication between the virtual computer and the host operating system by using the high-level Tcl language that openMSX provides. It goes without saying that you must know how to use the Tcl language to use this feature.
Note that this is not intended to be used as a drop-in replacement for resource-intensive hardware like VDPs. Tcl is overall a very slow language, but a programmable device opens up possibilities for using openMSX as a development tool that were not possible before.
Note there's some overlap between this device and the debug watchpoint add read_io/write_io
command. Both can be used to make Tcl react to I/O read/write operations. This
device is more suited for completely new functionality. The debug command is
more suited to intercept communication with existing MSX devices.
To enable the programmable device, insert the programmabledevice
extension. To do this when starting openMSX, simply add
-ext programmabledevice to the openMSX command line. If openMSX is
already running, you can use the
ext console command.
Device ports are a list of I/O ports connected between the guest computer and the Tcl environment. This means that anything a Z80 assembly program sends to one of these I/O ports using an OUT instruction automatically calls an "output callback" (a Tcl procedure) to receive the data on the Tcl side. You must declare your own output callback, otherwise the programmable device will do nothing when it receives a byte. Your callback must have two parameters: port and value (2 8-bit values) the return value from this callback is ignored.
Alternatively, anything a Z80 assembly program reads from one of these I/O ports using an IN instruction automatically calls an "input callback" on the Tcl side. That callback produces the value that will be received by the Z80. You also must declare your own input callback, otherwise the programmable device will return 0xFF. An input callback receives a (8-bit) port number as the only parameter, and it must return an 8-bit value.
The third kind of callback you can create is the "reset callback". This one has no parameters and the return value is ignored. It can be useful for setting back an initial state when the MSX reboots.
You can check the 4 settings that Programmable Device uses with the help command, but briefly:
tracks I/O ports 6 and 7.
connects the reset event with your previously declared "my_reset_proc" callback.
connects the "OUT instruction" event with your previously declared "my_output_proc" callback.
connects the "IN instruction" event with your previously declared "my_input_proc" callback.
openMSX includes the SDCC Debugger called sdcdb, a Tcl script that mimics GDB (GNU Debugger) and allows you to inspect programs compiled with the Small Device C Compiler (SDCC) from the console. You just need to compile your SDCC code with the -debug flag to create a CDB file with symbols and their respective addresses and then call sdcdb open <directory> where the CDB file and source code are. Now you can inspect the program while it executes. For instance, to create a breakpoint at file main.c, line 155 from your source code, you can type:
A SDCDB breakpoint is a regular breakpoint and it can be listed with the debug breakpoint list command. When a breakpoint is triggered, you can inspect the source code around it with command sdcdb info. There are two commands that executes code step by step. The first is sdcdb step, which executes C code line by line and goes inside function calls. It is equivalent to the step_in command from the console. The second is sdcdb next, which executes C code line by line but doesn't go inside function calls. It is equivalent to the step_over command from the console. The useful sdcdb laddress <address> will display source code under the given memory address since sdcdb is aware of the program's source code, like GDB. You can type help sdcdb for more details or check out the comments in sdcdb.tcl script for more examples.
Because openMSX is still in heavy development, feedback and bug reports are very welcome!
If you encounter problems, you have several options:
#openMSX on
libera.chat
and ask your question there. Also reachable via webchat! If you don't get a reply
immediately, please stick around for a while, or use one of the other contact
options. The majority of the developers lives in time zone GMT+1. You may get
no response if you contact them in the middle of the night... openmsx-user mailing list.
If you want to address the openMSX developers directly, post a message to the
openmsx-devel mailing list.
More info on the
openMSX mailing lists,
including an archive of old messages, can be found at SourceForge.
In any case, try to give as much information as possible when you describe your bug or request.